What matters
The upcoming fourth bitcoin halving event, historically preceded by an increase in bitcoin’s price, underscores its growing scarcity and heightened investor interest, potentially leading to a surge in market activity and value.
What matters next
As bitcoin mining becomes more challenging and block rewards diminish, an equilibrium may emerge, potentially stabilizing bitcoin’s value. Approaching the bitcoin limit could see it and related products such as ETFs rely less on popularity, behaving more like fiat currencies in terms of practical use and stability.
So, what exactly does halving entail, and why is there such a buzz surrounding it? The term itself evokes the intrigue of a suspenseful horror film, one that could be straight out of a Stephen King story.
The halving
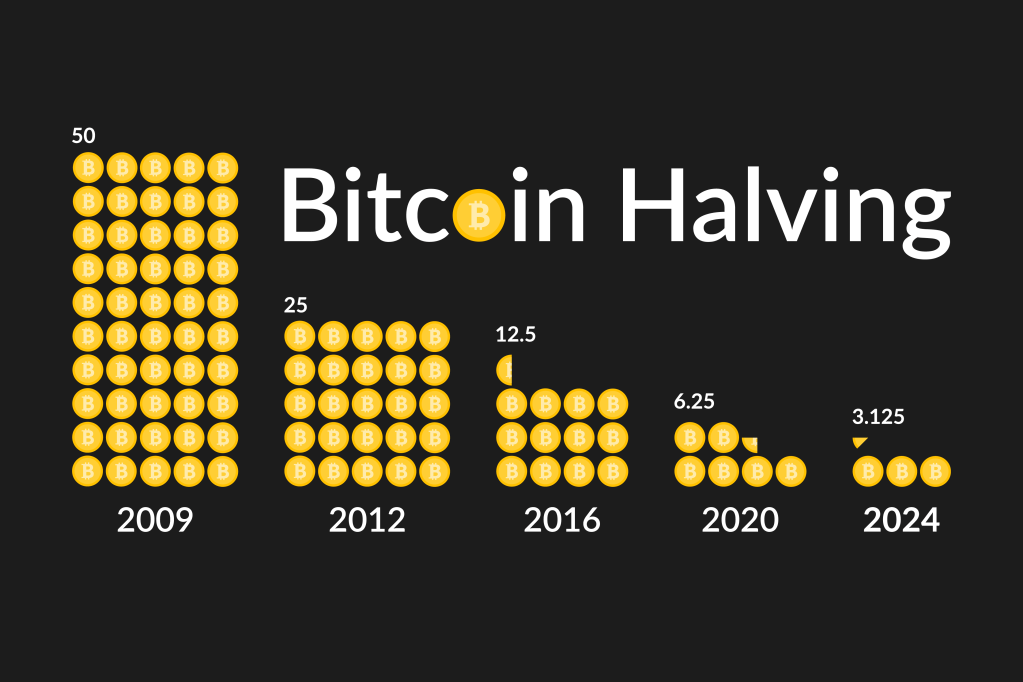
The halving (which occurs roughly every four years, or, more precisely, every 210,000 mined Bitcoin blocks) will see the reward for a successfully mined block reduced by 50% from 6.25 to 3.125 bitcoins – which, at current prices, translates to a drop in the mining reward from around $425,000 to $212,500.
This will be the fourth bitcoin halving. The first occurred in November 2012, the next in July 2016, and the most recent in May 2020. History shows that the price of bitcoin increases after each halving. This positive price movement can be attributed to several factors. First, the reduction in the supply issuance rate emphasises bitcoin’s scarcity (many saying that this makes bitcoin scarcer than traditional safe-haven assets such as gold and real estate), which can drive up demand and consequently increase its price. Second, the halving brings attention to the crypto sector, attracting new investors and contributing to increased trading activity.
The Bitcoin software was designed with this “automatic” halving feature at its core – a built-in deflationary mechanism where the number of new bitcoins put in circulation through mining reduces over time and ensures that the total number of bBitcoins possible (…ever) is capped at 21 million. Currently there are around 19.6 million bitcoins in circulation, so roughly 93.6% of the total possible bitcoin supply has been mined since the cryptocurrency’s launch in 2009.
Rising price of bitcoin
Regulatory developments
The recent rises (to record levels) in the price of bitcoin is to do with a number of factors which are not related to the impending halving in April 2024. These include;
- positive regulatory developments in the UK;
- the sea-change demonstrated by increasing wholesale and institutional market interest in digital assets;
- approval in the US of spot bitcoin (and shortly ether) Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs);
- and the notice issued by the London Stock Exchange that it would accept applications for spot bitcoin ETFs.
Bitcoin ETF
A bitcoin ETF is a regulated financial product, listed and traded on established venues, that allows retail investors to gain exposure to the price movements of bitcoin without actually holding the asset itself. The US SEC approved the first 11 bitcoin spot ETFs in the US on January 10, 2024. Bitcoin futures ETFs had already been trading in the US since 2021. Unlike a futures-based ETF, a spot ETF owns actual bitcoins.
There has been significant media interest in bitcoin ETFs since they were launched, particularly around “inflows” (investments into bitcoin ETFs) and “outflows” (withdrawals from bitcoin ETFs). As one might expect, initial inflows were significant. Since then, the headlines have been swinging from mentioning material outflows to “winners and losers” in the competition for investment.
In other words, while inflow may have been positive in some weeks, some bitcoin ETFs have suffered redemptions while others have either picked up those redemptions as new investments or established new investments. Trading volumes in bitcoin ETFs had been falling (slowly) in March, too. The price of bitcoin peaked around March 12th, but dropped since and is now trading relatively flat (even if it remains up over 50% from a year ago).
Bitcoin demand from public traded companies
The other major activity explaining the increase in the price of bitcoin is demand from publicly traded companies investing heavily in the cryptocurrency. MicroStrategy, Inc (NASDAQ: MSTR), for example, is a technology business specialising in artificial intelligence-powered enterprise analytics software and services, but is also estimated to have accumulated 214,246 bitcoins as of March 2024 (that’s $14,837,092,539 at current prices).
As a result, retail investors have been attracted to such bitcoin ‘proxy stocks’ to benefit from the surge in its price without investing in bitcoin directly. This, in turn, helps to explain the rise in the stock price of MicroStrategy, which is up about 500% during the past 12 months.
The economics is simple when you think about it: with all this new interest (including from bitcoin ETFs) there is greater demand for bitcoin purchases; increased demand of bitcoin drives the price higher; and the supply of bitcoin is limited.
After the halving
So, what will happen after this impending bitcoin halving event? Bitcoin blocks are becoming increasingly difficult to mine – which is another way of reducing supply – and as rewards continue to fall for mining a Bitcoin block, perhaps there is an equilibrium that will be reached. Perhaps also (as we get closer to the limit of the number of bitcoin) bitcoin and all associated products such as ETFs will cease to be so reliant on popularity and media exposure and demonstrate more characteristics of fiat currencies in application, use, and relative value.
With all this interest and activity, it’s very important not to forget the basics of any crypto ownership; always remember: Not Your Keys, Not Your Crypto.
Prakash Kerai is a partner, he supports organizations on their technology and FinTech arrangements. Sam Tyfield is co-head of the Blockchain & Digital Assets team.